Do you want to know the answer to the question “How are baby bunnies born”? Rabbits are a popular pet for many people, and like any other animal, they reproduce and bring forth young. In this article, we will discuss the process of how baby bunnies are born, from conception to delivery. We’ll also look at the care of newborn bunnies and what to expect during the first few weeks of life. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how baby bunnies are born and how to care for them.
What is a Baby Bunny?

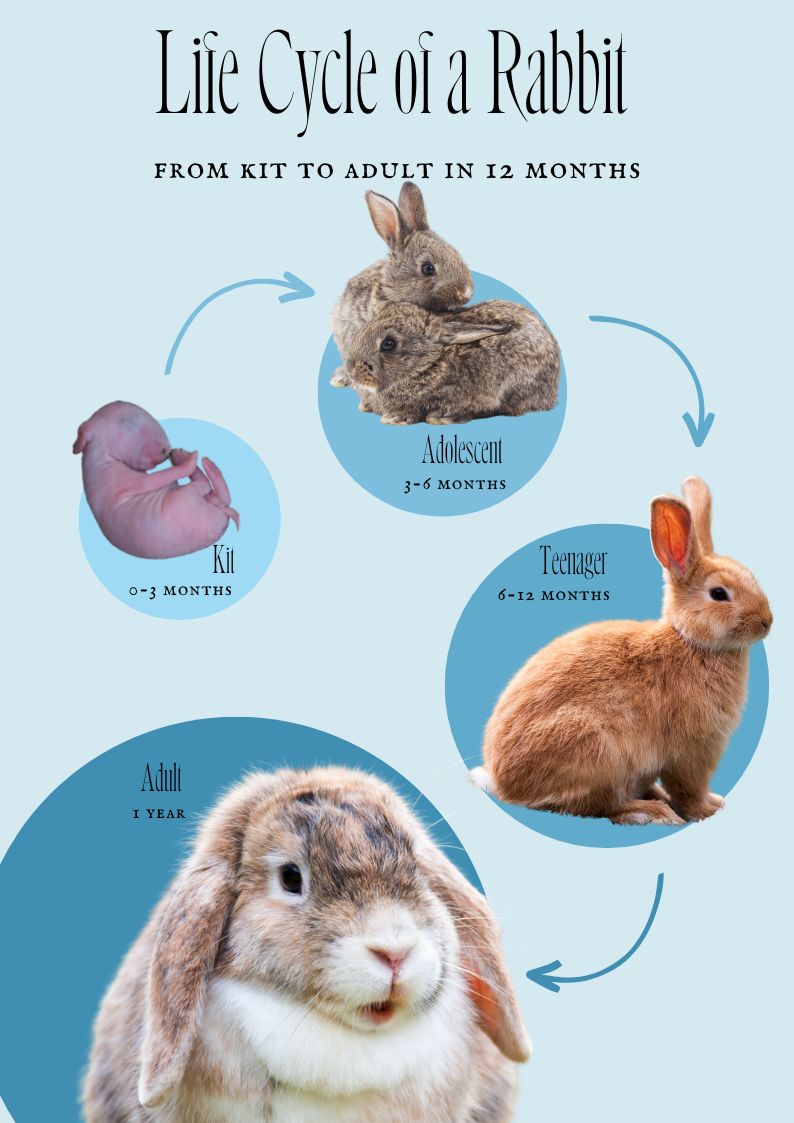
A baby bunny is also known as a kitten, kit, or bunny. A newborn bunny is born hairless, its eyes and ears closed, and is totally dependent on its mother for survival.
- Baby bunnies are born blind and deaf.
- Baby bunnies are born with no fur and are blind, deaf and helpless.
- A baby bunny is a newborn rabbit that is usually hairless, blind, and weighs only a few ounces.
- Baby bunnies are weaned at about 8-10 weeks, although they may continue to nurse until they are 12-16 weeks old.
- Baby bunnies will start eating solid food at around 3-4 weeks old, although they may still nurse from their mother.
- Baby bunnies are vulnerable to predators and must rely on their mother’s protection.
- Baby bunnies are able to hop at around 4-5 weeks old.
- Baby bunnies will begin to explore their surroundings and become more independent at 8 weeks old.
Baby bunnies develop rapidly due to their short lifespans, so it’s important for them to get the proper nutrition to ensure a healthy start to life. Knowing how do bunnies have babies is essential to ensure the health of your rabbit family.
How do Bunnies Have Babies?
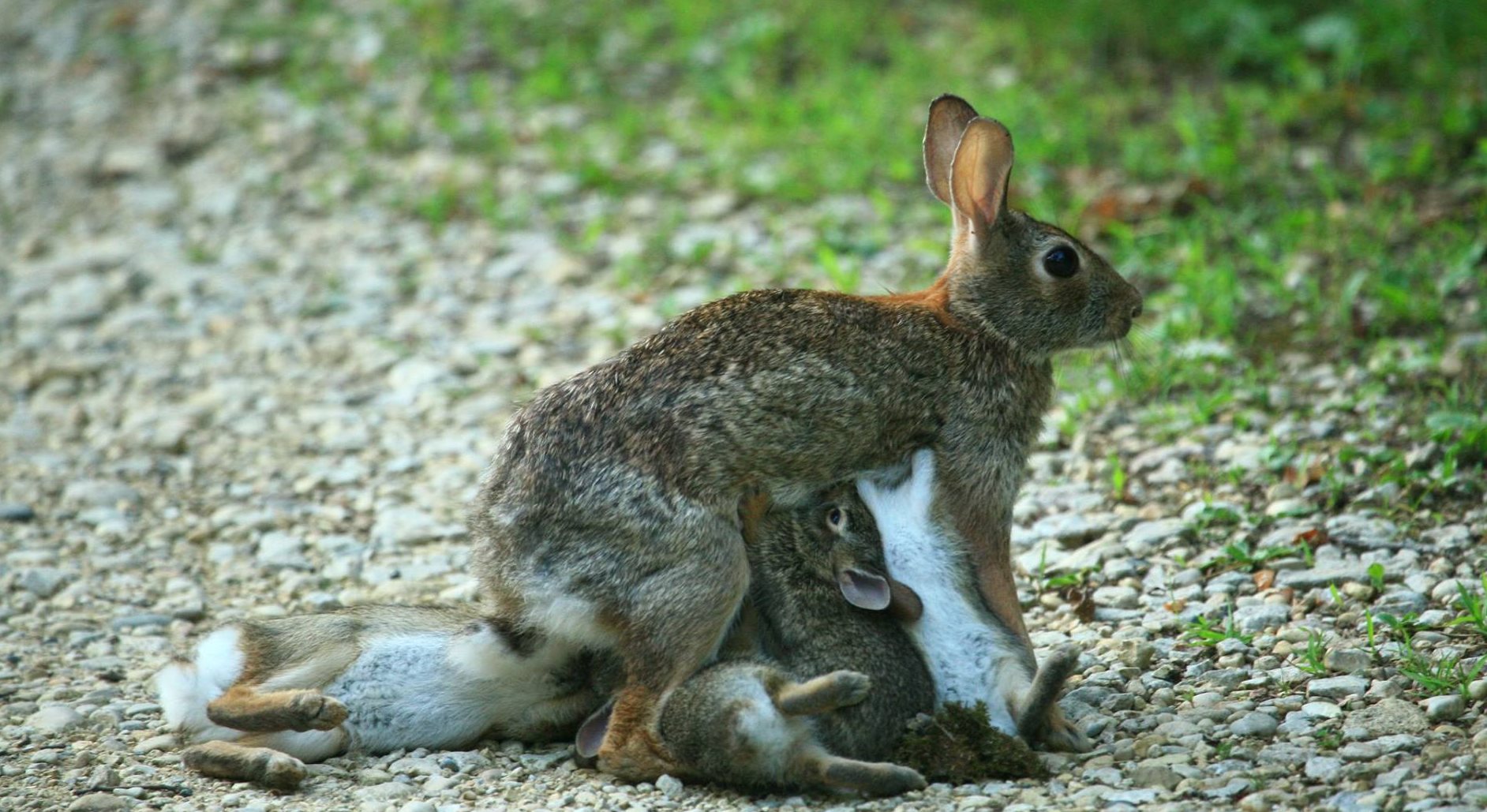

Female rabbits, or does, reach sexual maturity at around 4-6 months old. Breeding usually takes place between March to September, and the mother rabbit can have up to three litters in a year.
Gestation in rabbits is between 28-31 days, and a doe can give birth to up to 12 babies, known as kits. When the kits are born, they are blind and hairless, and the mother rabbit will need to keep them warm. She will not feed them until they are around four days old.
The kits will start to open their eyes after 10 days and they will start to explore their surroundings when they are around two weeks old. When the kits are 3-4 weeks old, they will start to eat solid food, and will start to leave the nest when they are about five weeks old.
At this point, the mother rabbit will not feed them anymore, so the kits will need to find their own food. When the kits are eight weeks old, they will be fully weaned and ready to live independently.
If the mother rabbit does not feed the babies for some reason, then the kits will need to be hand-reared with a special milk replacer. As this process is quite difficult, it is best to leave the kits with the mother rabbit and ensure that she is in good health.
The Reproductive Cycle of a Rabbit
Mating
Female rabbits reach sexual maturity around 4-5 months of age and males around 6-7 months. Rabbits mate year round and a female can be impregnated again within minutes of giving birth.
Pregnancy
A rabbit’s gestation period is 28-31 days long. While pregnant, the female will continue to eat and groom as normal and her abdomen may swell slightly.
Delivery
Rabbits are excellent mothers. Before giving birth, the female will begin to build a nest in the form of a shallow depression in the hay or straw, lined with fur pulled from her own body. The female will give birth to a litter of usually 4-12 young, and she will nurse her babies several times throughout the day.
At birth, baby rabbits are blind and furless, but they will quickly begin to grow and develop. The babies can leave the nest at 4 weeks of age, but they will stay close to their mother until they are 8 weeks old.
Baby Bunny Development
After conception, female rabbits will gestate for an average of 30 to 32 days. During this period, a developing embryo will quickly form from a single cell into a fully formed rabbit.
First Week
The fertilized egg implants in the uterine wall and the embryo begins to form. By the end of the first week, the embryo has developed a rudimentary heart and blood vessels and is approximately 0.04 inches in length.
Second Week
By the second week, the embryo has grown to 0.12 inches and the heart begins to beat. The eyes, ears, and limbs are also beginning to form. The skeleton is still soft and pliable.
Third Week
By the third week, the skeleton is becoming more defined and the eyes, ears, and limbs are more developed. The heart is now beating more strongly and the fetus is approximately 0.32 inches in length.
Fourth Week
At the end of the fourth week, the embryo is roughly 0.63 inches in length and is well-developed. The eyes, ears, and limbs are almost fully formed and the heart is beating strongly.
Fifth Week
By the fifth week, the fetus is now fully formed and ready to be born. The eyes, ears, and limbs are fully developed and the heart is now beating strongly. The fetus is approximately 0.87 inches in length.
Sixth Week
At the end of the sixth week, the fetus is now ready to be born. The eyes, ears, and limbs are fully developed and the heart is now beating strongly. The fetus is approximately 1.19 inches in length.
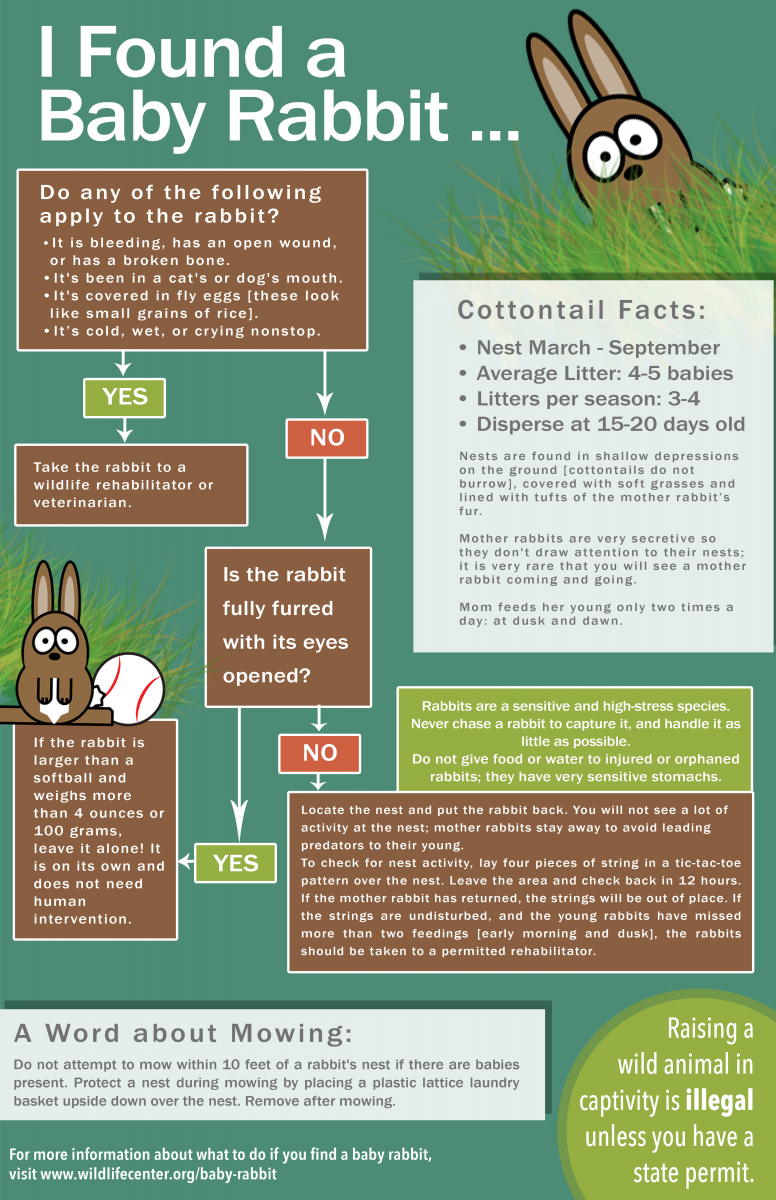
What to do if Mother Rabbit is Not Feeding Babies

Immediate veterinary care is essential if the mother rabbit is not feeding her babies. If a mother rabbit does not feed her babies, it could be due to a medical issue, or the mother may be rejecting the babies.
- Take the babies to the vet to check for any underlying medical issues.
- Check that the babies are properly hydrated and do not appear to be malnourished.
- If the mother rabbit is rejecting the babies, try to encourage her to feed them. Ensure that the environment is as stress-free as possible and that she is getting enough food and water.
- If the mother rabbit is still not feeding the babies, you will have to provide them with formula.
- For newborns, use a commercial rabbit formula available from pet stores. For older rabbits, you can use a combination of evaporated milk, yogurt, and boiled egg yolk.
- Feed the babies every two to three hours and monitor them closely to make sure they are getting enough nutrition.
If you are unable to get the mother rabbit to feed her babies, it is best to seek advice from a veterinarian. They will be able to provide further guidance on how to best care for the babies.
How to Care for Baby Bunnies
- Keep them warm: Baby bunnies are born without fur and are very fragile. They should be kept in a warm area, preferably at least 80°F. If possible, use a heating pad set to the lowest setting.
- Provide a safe environment: Make sure the area they are kept in is free from any potential hazards. Keep other pets away and make sure the area is secure.
- Feed them: Baby bunnies need to be fed every two hours. Use a specially formulated milk replacer and feed them with an eyedropper or syringe. Avoid overfeeding and weigh them regularly to ensure they are gaining weight.
- Keep them clean: Change the bedding in their cage every two days and make sure to clean up any messes. Also, use a damp cloth to wipe down the baby bunnies every day.
- Socialize them: Baby bunnies need to be socialized to help them become more comfortable around humans. Handle them gently and often, and be sure to spend time talking and playing with them.
- Monitor them: Monitor the baby bunnies for any signs of illness or injury. If any signs are present, contact a veterinarian immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for baby bunnies to be born?
- Gestation period: The gestation period of rabbits is 28 to 31 days.
- Weaning period: The weaning period for baby rabbits is 6 to 8 weeks.
- Fertility: Female rabbits reach sexual maturity as early as 4 months of age and can have litters of 2 to 12 kits (baby rabbits).
Rabbits have a relatively short gestation period of 28 to 31 days. During this time, the female rabbit’s body will be preparing for the birth of its kits. Shortly before giving birth, the female rabbit will start to build a nest in a safe and secure area. After the gestation period is complete, the female will give birth to her kits.
Once the kits are born, the mother rabbit will nurse them for 6 to 8 weeks. During this time, the kits will grow rapidly, and the mother will teach them how to forage for food. Once the kits are old enough, the mother will start to wean them off her milk.
Female rabbits reach sexual maturity as early as 4 months of age and can have litters of 2 to 12 kits. The mother will typically have between 2 to 4 litters per year. After the kits are weaned, they will be ready to move out of the nest and start their own lives.
What is the Gestation Period for a Rabbit?
- Average Gestation Period: Rabbits have an average gestation period of 28-31 days.
- Variations in Gestation Period: Depending on the breed and size, gestation period may vary. Smaller breeds usually have a shorter gestation period than larger breeds.
- Factors Affecting Gestation Period: The gestation period of the rabbit can be affected by various factors such as age, health, nutrition, environment, etc.
- Signs of Pregnancy: Signs of pregnancy in rabbits include an enlarged abdomen, changes in behavior, and a decrease in physical activity.
- Litter Size: The average litter size for a rabbit is 4-7, although it can range from 1-15.
How many litters can a female rabbit have in one year?
A female rabbit can have up to five litters in one year, with each litter producing an average of five to six baby bunnies. The gestation period is 28 to 31 days, with a female capable of becoming pregnant again immediately after giving birth. The breeding season usually begins in March and continues until September, with peak activity in April and May.
How often do rabbits give birth?
- Average Gestation Period of Rabbits: Rabbits have an average gestation period of 28-33 days.
- Litter Size: Rabbits tend to have a litter size of 4-12 kits (baby bunnies).
- Frequency: Rabbits can give birth up to 4 times a year, but it is more common for them to give birth 2-3 times a year.
Note: It is important to note that a rabbit’s fertility decreases with age, so older rabbits may not have as frequent litters.
At What Age Are Baby Bunnies Able to Survive on Their Own?
Baby bunnies are typically weaned and ready to live independently at 8-10 weeks old. They should not be separated from their mother and littermates until this age or they risk not developing the skills they need to survive in the wild. Once they have grown old enough, they can be spayed/neutered and adopted out to loving homes.
Conclusion
Baby bunnies are born after a gestation period of 28-31 days. The litter size can vary from two to twelve, and they are born fur-covered and with their eyes closed. The mother rabbit will nurse and look after them until they are ready to venture out into the world. Knowing how baby bunnies are born can help you better understand and care for them.
